Inngest vs. Temporal: Which one should you choose?
As we build more sophisticated distributed systems, the complexity of managing state, handling failures, and orchestrating long-running processes has exploded. For years, developers have manually wired together queues, databases, and cron jobs to manage this, resulting in brittle, hard-to-debug systems.
The rise of AI and agentic workloads now magnifies the challenge with their inherently multi-step, stateful, and unpredictable processes. Orchestrating non-deterministic LLM calls, dynamic tool use, and long-term memory for an AI agent requires a level of resilience that traditional stateless architectures were never designed for.
This conflict and the need for different architectural patterns brought about the rise of workflow orchestration platforms, and choosing the right one is a major decision for many engineering teams.
Inngest and Temporal are both popular options for “durable execution,” a powerful standard that guarantees your code will run reliably to completion — even if it gets interrupted by a server outage or needs to wait for years. The magic of durable execution is that it allows you to write what looks like simple, sequential code while the program invisibly handles the immensely intricacies of persistence, retries, and long-running waits.
That said, Inngest and Temporal perform the trick in fundamentally different ways: one rooted in a dedicated cluster and stateful workers, while the other works in a serverless-first, event-driven model. Let’s drill into the differences and help you get the clarity you need to make the foundational decision that will shape your application’s scalability, operational overhead, and developer velocity.
Under the hood: How each platform delivers durable execution
To really master the Inngest vs. Temporal debate and how it affects your organization, you have to understand the platforms’ fundamentally different architectural philosophies. Temporal operates like a dedicated and stateful conductor for your application’s logic, while Inngest takes a serverless, event-driven approach that favors choreography over orchestration.
| Trait | Temporal | Inngest |
|---|---|---|
| Core model | Stateful clusters & workers (orchestration) | Serverless & event driven (choreography) |
| State persistence | Comprehensive event history in a database you manage or provision | Managed by the Inngest platform, obscured from the developer |
| Execution model | Workers pull tasks from a central queue run by the cluster | Functions are invoked through HTTP in response to events |
| Agent communication | Workflow-to-workflow calls, signals, or child workflows | Event-based; one agent emits an event, another consumes it |
Temporal is built on a server-based model you can self-host or use through their cloud. The core platform consists of the Temporal Cluster, a set of services that continually track the state of every process, and Worker Processes. Workers are long-lived processes that execute two types of code: Workflows, which define the orchestration logic, and Activities, which are the individual, sometimes non-deterministic steps (like an LLM call).
Temporal records every state change in Event History, a complete append-only log that allows the platform to recover and resume a workload from its exact point of failure. For AI, this model provides immense control for orchestrating complex multi-stage pipelines, such as for model training or a predictable, multi-step agentic chain of thought.
Inngest adopts a serverless first, event-driven philosophy.
Instead of managing a persistent cluster, organizations organize code into functions, which Inngest triggers in response to events. Users create the functions using durable steps, or atomic units of work the platform automatically retries and persists on your behalf. Inngest handles all the underlying queueing, state, and retries behind a simple API, invoking your functions via HTTP.
This event-driven model makes the platform a natural fit for building reactive AI agents that must respond to asynchronous events like a user message or database update. Organizations model agent–to-agent communication simply by having one agent emit an event that another’s function consumes, and Inngest provides features specifically for human-in-the-loop AI workflows.
Scalability and production readiness for AI workloads
Moving an AI application from a prototype to a production system introduces a whole new set of requirements. Here’s where the theoretical beauty of a workflow engine meets the harsh realities of infrastructure management, observability, and cost.
When considering which platform to use, teams building with AI should understand the trade-offs and different ways Temporal and Inngest address these concerns.
Let’s break it down.
Infrastructure requirements
With the open-source version of Temporal, your team takes direct responsibility for the orchestration infrastructure. You deploy and scale a Temporal Cluster, manage its underlying database, and operate a fleet of Worker Processes that execute your code. However, it’s important to note that with Temporal Cloud, this is not the case (Temporal Cloud is a managed service).
This setup gives you ultimate control — you can co-locate workers with GPUs for low-latency inference or deploy into specific regions to meet data residency requirements. This feature enables large enterprises with dedicated platform teams to tune the environment precisely for their workloads.
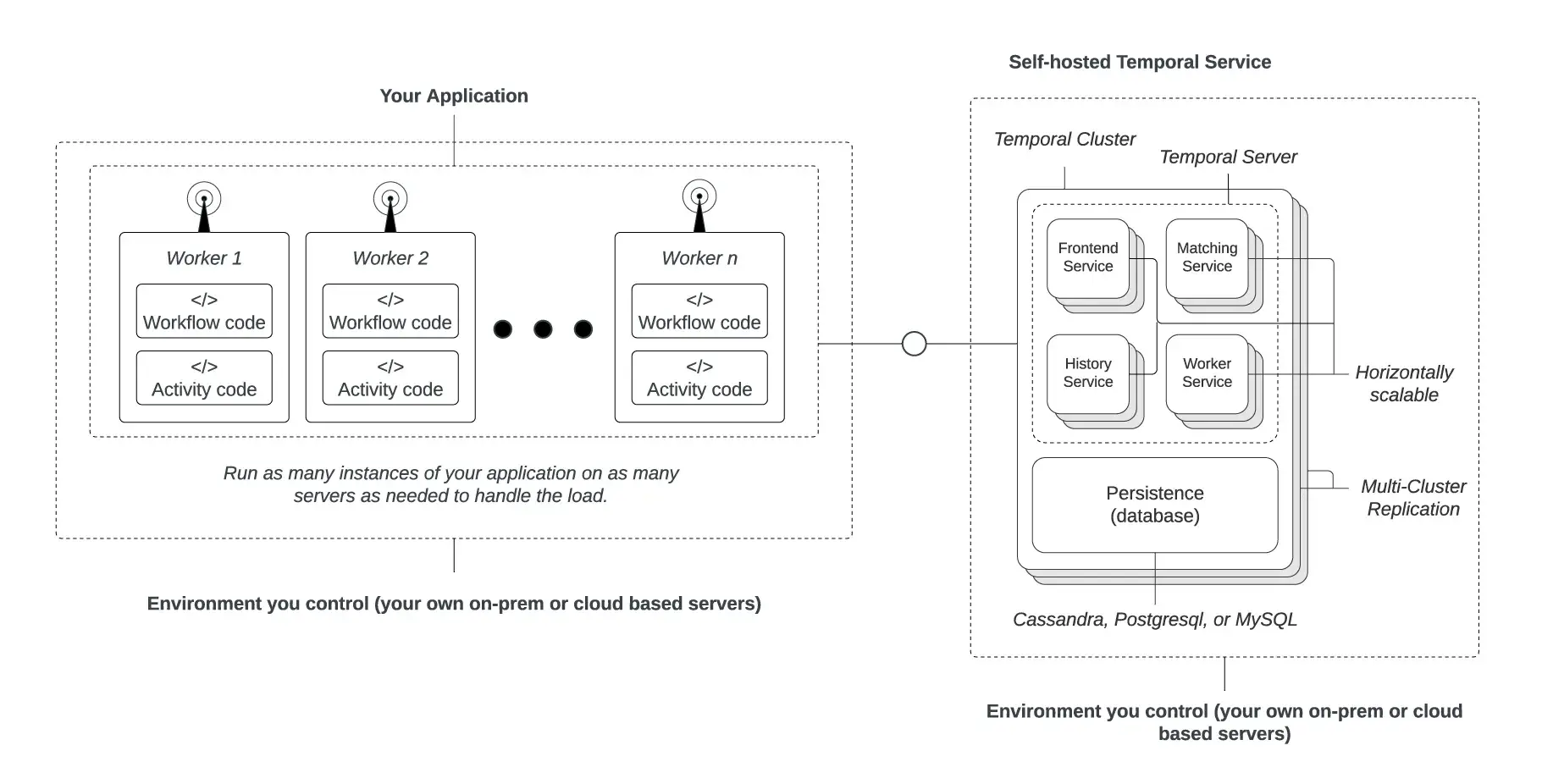
Source: Temporal Documentation
Inngest, however, abstracts this infrastructure away, dramatically reducing your operational overhead. Your team writes functions and deploys them to the organization’s preferred environment, whether on a serverless platform like Vercel or a container on your own cluster.
Inngest invokes these functions through secure HTTP calls, managing the entire durable execution and queueing system as a service. You don’t manage the orchestration engine’s uptime; instead, you get to focus solely on the logic that calls your AI models. The serverless-first approach lets teams move faster and scale without needing to become experts in distributed systems.
Monitoring and observability
The Temporal platform provides web and command-line interfaces that enable organizations to inspect the event history of any workflow, which is invaluable for debugging the state of a specific execution.
However, for comprehensive and system-wide observability (including metrics, distributed tracing, and logging), you’ll need to integrate and manage external tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and Jaeger. In essence, you’ll have to build your own pane of glass.
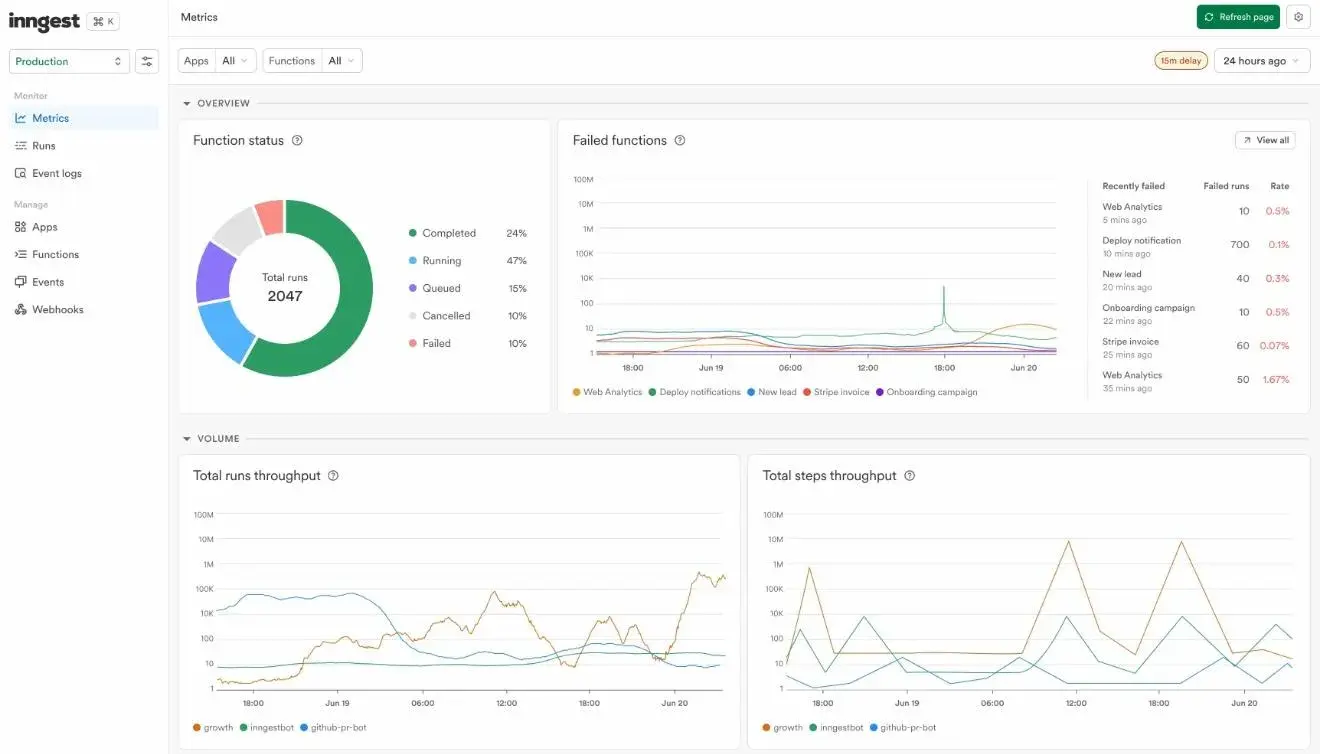
Source: Inngest Documentation
On the other hand, Inngest integrates observability as a core part of its product. It’s dashboard provides live visual tracing for every workflow, including specific instrumentation for AI. Developers can instantly inspect the prompts and responses from LLM calls, see token counts, and debug agentic steps in real time.
This built-in visibility significantly accelerates the team’s output, as the transparency removes the need to build and oversee custom observability tools. Even better, Inngest’s powerful replay functionality allows your team to recover from errors by re-running thousands of failed workflows in bulk after a bug fix — a much more manual process in other systems.
Cost analysis
Your spending on Temporal will directly reflect your infrastructure footprint and operational effort. You will simply pay for the compute and storage resources for the cluster and workers, making it potentially more cost-effective for high-volume and predictable workloads where you can optimize resources — however, this means you’ll also pay for idle capacity.
Pricing for Inngest follows a usage-based model, which aligns well with the unpredictable nature of AI workloads. You only pay for execution, not for idle infrastructure. This can be a significant advantage, particularly when using serverless platforms where features can pause your function and offload the long wait for an AI model’s response, directly reducing your compute bill.
Making the choice: Control vs. convenience (comparison chart)
To bring it all together, the choice between Temporal and Inngest often comes down to a trade-off between control and convenience. Factors like your team’s size, operational expertise, and required iteration speed heavily influence the right decision.
Take a look at some of the key differentiators between the two platforms for AI-focused teams:
| Feature | Temporal | Inngest |
|---|---|---|
| Developer velocity | Moderate - Steeper learning curve to understand workers | High - Intuitive SDKs and simpler event-driven model |
| Operational overhead | High - You oversee the cluster, database, and workers | Low - Serverless-first approach and platform managed for you |
| Scalability and control | High - You control and adjust all infrastructure components | High - Scales automatically with built-in flow control |
| Observability | Build-your-own - Requires integrating external tools | Built-in - Out-of-box tracing, metrics, and AI-specific tools |
| Cost model | Infrastructure-based - Pay for provisioned resources | Usage-based - Pay for what you use; good for varied workflows |
| Enterprise readiness | Strong - Full control for custom compliance | Managed - SOC 2, HIPAA, and others offered as a service |
Ultimately, choosing between Inngest vs. Temporal is less about features and pricing and more about architectural philosophy and organizational goals. Do you need the fine-grain control of Temporal, or the hands-free speed of Inngest?
Real-world applications and use cases: Where each platform shines
A workflow engine’s true value depends on its application. Although both Temporal and Inngest can orchestrate complex processes, their different architectures make them better suited for specific types of AI workloads.
The choice hinges on whether your organization prefers systems more like a meticulously planned stage production or a reactive improv performance. Here, we’ll explore some common scenarios to illustrate how each platform shines.
AI agent orchestration and multi-step reasoning
For structured, multi-step workflows, like an agent following a predefined “chain of thought” to book a complex trip, Temporal provides complete, nuanced control. You can define the entire plan as one auditable Temporal Workflow, where each step is an Activity.
The workflow’s state is centrally managed and fixed, which is ideal for processes where the execution path is known and must be strictly followed.
Inngest excels in orchestrating more dynamic and reactive agents through choreography. Its event-driven model is perfect for scenarios where an agent must respond to unpredictable external events.
Source: Inngest
For example, an AI agent monitoring a codebase could emit a “vulnerability detected” event. An Inngest function would consume this, trigger an LLM to analyze the vulnerability, and then pause to wait for a developer’s approval before creating a pull request. This reactive model is a natural fit for building collaborative, multi-agent systems where agents respond to each other’s actions.
Enterprise AI automation and intelligent processes
In large enterprises, AI automation often involves integrating with a complex landscape of legacy systems, modern microservices, and third-party APIs.
Temporal is a strong choice for these environments. For instance, a Temporal workflow could orchestrate a multi-day process that pulls a PDF from a legacy file share, sends it to a cloud Optical Character Recognition (OCR) service, passes the text to an AI model for summarization, and finally archives the results. Temporal’s industrial-strength durability guarantees this long-running, cross-system process will complete reliably.
Real-time AI vs. batch processing
Inngest’s low-latency, event-driven architecture makes it strong for real-time AI applications like customer service chatbots. When a user sends a message (an event), an Inngest function can instantly trigger, call an LLM to generate a response, and stream the answer back. The entire interaction is a short-lived, reactive workflow where responsiveness is critically important.
Temporal, however, is a beast for large-scale batch processing. If your organization needed to generate unique descriptions for a catalog of 100,000 products, you could initiate a single parent workflow that spawns thousands of child workflows. The massive job could run for days, and Temporal’s platform would reliably manage the state and recovery of every single execution to ensure no work is lost.
Startup vs. enterprise AI deployment
Because startups typically prioritize operational overhead and developer velocity, Inngest is usually the best choice. Its excellent dev experience, built-in observability, and serverless model enable a small team to build and ship complex AI features in days instead of weeks.
For enterprises, the control, deep integration, and proven reliability at massive scale are the primary reasons to choose Temporal. The large organizations often have dedicated platform teams to manage a self-hosted Temporal cluster, along with the security, compliance, and performance tuning.
Final thoughts: Choosing your AI orchestration platform
The verdict between Inngest and Temporal is a choice between two powerful but different philosophies for building reliable applications. Don’t decide based on a generic list of features, but rather by your organization’s specific priorities and experience, combined with the architectural demands of your AI workload.
As we’ve covered, Inngest provides a serverless-first, event-driven model that prioritizes developer velocity and is ideal for reactive AI features. Temporal offers fine-tuned control through a self-hosted or managed cluster for enterprises that need to orchestrate mission-critical processes with absolute certainty.
But what if your needs go beyond simply adding workflows to an application? What if you are actually building the resilient, distributed, and agent-native application itself?
Akka presents a compelling and powerful alternative for organizations building sophisticated agentic AI systems. Where Inngest and Temporal provide top-down orchestration, Akka supplies a bottom-up framework for building autonomous, stateful agents from scratch.
Akka enables you to model each agent as a lightweight, stateful actor with its own behavior and memory. These actors communicate asynchronously, forming a highly scalable and resilient system. Akka’s event-driven architecture and proven durable execution capabilities are purpose-built for the most demanding AI scenarios:
- Complex agent coordination: Imagine orchestrating a choreographed swarm of AI agents collaborating on a complex problem. With Akka, each agent (actor) can communicate directly and reactively, enabling more complex and emergent behaviors than a rigid workflow engine can easily manage.
- Real-time AI processing: When an AI system has to process high-throughput data streams, like real-time video analysis or IoT sensor data, Akka’s high-performance, brokerless messaging provides a level of responsiveness that is difficult to achieve with traditional queue-based or HTTP-based orchestration.
Ultimately, while Inngest and Temporal are excellent tools for orchestrating workflows, Akka is the platform to choose when you need to build the highly available distributed foundation for your agentic system itself. If your vision involves millions of autonomous agents operating with extreme resilience and real-time responsiveness, then Akka provides the clear path forward.
Posts by this author


